
Multi-tenancy refers to an architecture where a single software instance serves multiple users or ‘tenants’. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants. In the context of cloud services, multi-tenancy means that a single server or instance can handle the needs of multiple tenants, with each tenant’s data isolated from others.
This architecture’s primary importance lies in its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It allows for maximum utilization of resources, eliminating the need to set up new physical infrastructure for each tenant. This leads to a significant reduction in costs and makes scaling easier, contributing to overall business agility.
Multi-tenant software is designed to host multiple tenants sharing the same infrastructure. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, SalesForce, etc., are popular examples of multi-tenant architecture. Redis Enterprise Cloud is a multi-tenant service with over 500,000 Redis databases sharing the Redis Cloud platform, serving different tenants. However, it’s worth noting that single tenancy is also an option for those needing more customized environments.
Redis Enterprise software allows you to create a multi-tenant environment on-premises or in any infrastructure you control, which is particularly beneficial in a cloud computing setting. But why would you need such an environment?
A multi-tenant environment can save you time and money if your organization develops its own in-house applications and microservices. A multi-tenant architecture eliminates the setting up of new physical infrastructure for your software and installing new supporting software (a database, for example) in your development, testing, and production environment. It enables you to execute multiple development efforts and testing cycles in parallel with little effort. This can be particularly advantageous for the current tenant user. However, if a specific customer has requirements for data isolation or unique resource requirements, a single-tenant approach may be more suitable. This is beneficial if a single instance of a particular environment is needed for targeted deployment or analytics.
A multi-tenant architecture and a multi-instance architecture have notable differences. In the latter, you install a new software instance for each tenant. The picture below illustrates an example of multi-instance architecture for Redis. In this scenario, you spawn a new Redis instance for every tenant, accommodating the need for tenant data segregation. As the number of your tenants grows, the complexity of deploying, monitoring, maintaining, and upgrading multiple software instances grows exponentially.
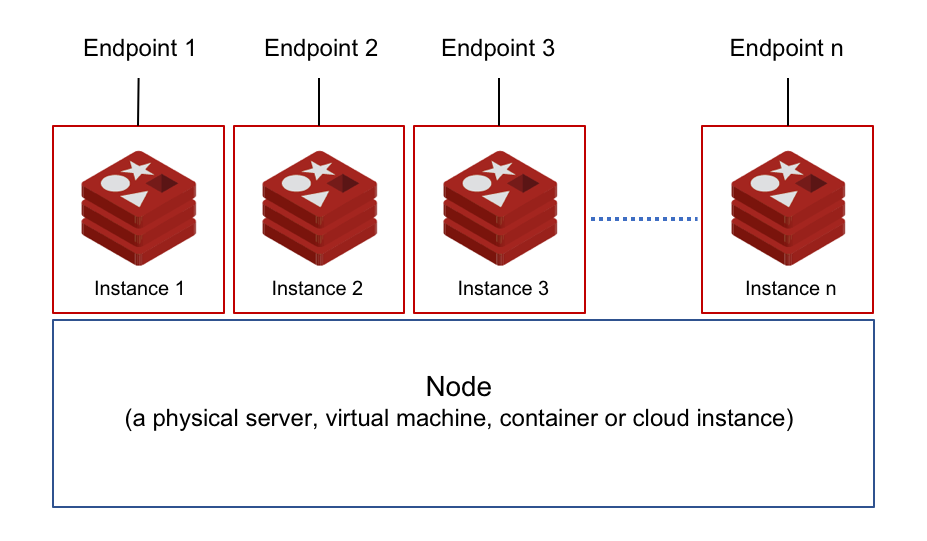
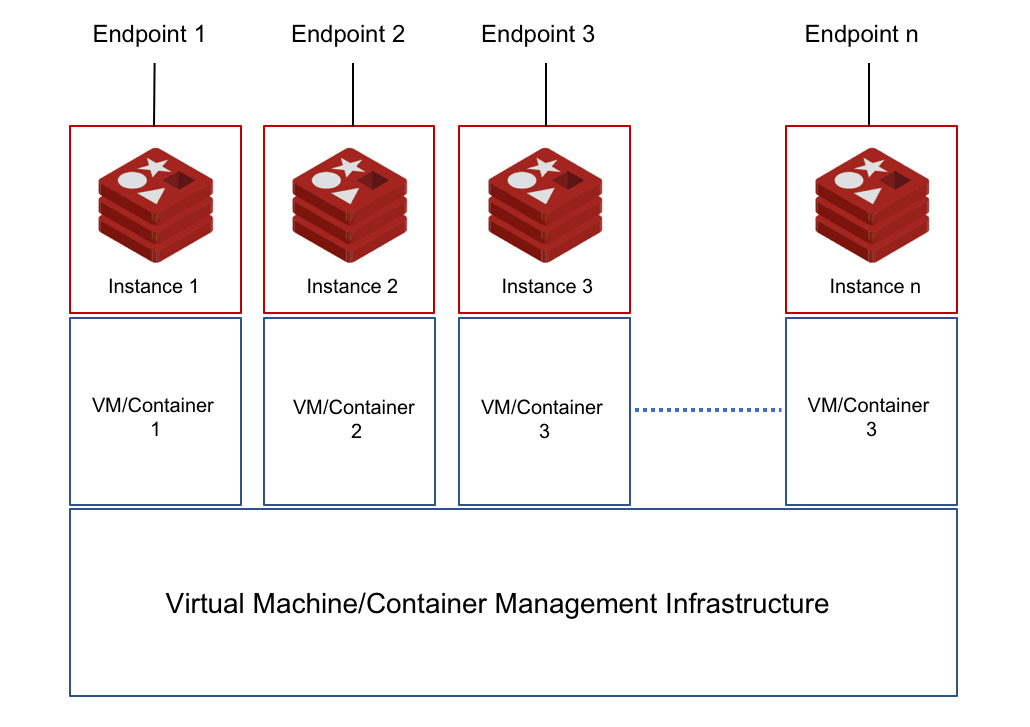
In this case, you deploy Redis as a container or a virtual appliance and allow the underlying management solution to spawn a new Redis instance. Multi-tenancy is achieved at the server/infrastructure layer, maintaining tenant isolation. In many ways, this technique of achieving multi-tenancy is not very different from the multi-instance setup. While the management layer reduces the complexity of provisioning and starting a new Redis service, you still have the same number of Redis services to monitor and manage. Typically, service providers like Redis-as-a-Service vendors such as Elasticache, Azure Redis, Google Redis, and Heroku Redis follow this method. These solutions are priced per Redis instance. The effects of scale and scope economies benefit these service providers more than you.
Redis Enterprise offers software multi-tenancy in which a single deployment of Redis Enterprise Software (often deployed as a cluster of nodes) serves hundreds of tenants. Each tenant has its own Redis database endpoint completely isolated from the other Redis databases, providing an efficient multi-tenant database setup.
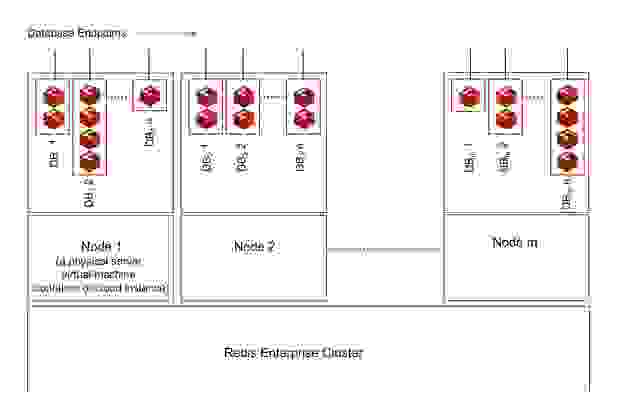
When you deploy Redis Enterprise in your data center, private cloud, or virtual private cloud, you benefit from the scope economies of the multi-tenant architecture. With a single Redis Enterprise cluster of a few nodes, you can support your development and testing efforts and then take it to production, accommodating different requirements of the different tenants.
Redis Enterprise architecture implements multiple layers of abstraction to deliver multi-tenancy, high availability, linear scaling, high throughput, etc. Redis Enterprise architecture is comprised of the following components:
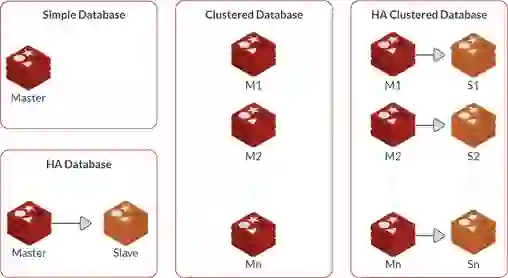
You may deploy multiple databases in a Redis Enterprise cluster; you are only limited by the total memory size. Every database endpoint has an FQDN. The zero-latency proxies on all of the nodes in a cluster can redirect client requests to the appropriate primary (master) database.
Redis Enterprise’s multi-tenancy solves many problems:
Redis Enterprise is a market-proven, multi-tenant solution. Redis Cloud is indeed Redis Enterprise’s multi-tenant service. Built-in controls within Redis Cloud ensure that all databases’ throughput and latency requirements are being met, while being shielded from “noisy neighbors” and while staying highly available in scaled out, distributed environments.
Redis runs more than 500,000 database endpoints on all the popular public cloud platforms: AWS, Azure, GCP and SoftLayer. Redis Enterprise Software is deployed as a multi-tenant software in over 300 enterprises. Read our documentation to learn how to create and maintain databases in a multi-tenant environment.
While multi-tenancy offers numerous advantages, it also comes with potential challenges, like data privacy, noise from other tenants, and resource allocation. Redis Enterprise has developed features to address these issues.
Data isolation is meticulously maintained in Redis Enterprise’s multi-tenant environment, ensuring that each tenant’s data remains invisible to others. Redis Enterprise also has mechanisms to handle “noisy neighbors”, ensuring that the activity of one tenant does not negatively impact others. The resource allocation is carefully controlled to maximize infrastructure utilization and to avoid any one tenant monopolizing shared resources.
Redis Enterprise has been successfully deployed in numerous organizations. For instance, a large e-commerce company might use multi-tenancy in Redis Enterprise to handle data for different departments, such as sales, marketing, and inventory, each acting as a different tenant.
Similarly, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider might deploy Redis Enterprise to manage data for different clients. Each client would be a different tenant, with their data isolated from others. In such scenarios, Redis Enterprise’s multi-tenancy helps maintain data privacy while ensuring efficient resource utilization.
Security is a paramount concern in any multi-tenant environment. Redis Enterprise is designed with several security measures in place. Data isolation between tenants is strictly enforced, ensuring that each tenant’s data remains invisible and inaccessible to others.
Additionally, Redis Enterprise deploys security measures to protect against potential breaches. This includes strong access controls, regular security audits, and the latest encryption standards to secure data both in transit and at rest. This provides an extra layer of assurance for businesses and helps maintain trust in the multi-tenant setup.