
Securing your data is increasingly critical as cyber attacks, security breaches and unauthorized access to data continue to escalate. Redis Enterprise provides advanced security controls to help simplify compliance with self imposed or regulatory compliance requirements such as HIPAA, FISMA, PCI, GDPR and so on.
events-and-webinars
What is Redis Enterprise?
First, for those of you who are not familiar, Redis Enterprise is a distributed NoSQL database engine that adds to the power of open-source Redis with an enhanced deployment architecture that delivers increased scalability, availability, security and lower total cost of ownership.
Redis Enterprise fully supports open-source Redis and Redis commands, data structures and modules. To start working with Redis Enterprise, existing applications need only change their connection string to point at Redis Enterprise databases.
Redis Enterprise is available for use in the cloud as a DBaaS platform under Redis Enterprise Cloud or Redis Enterprise VPC or it can be managed under your full control as downloadable software with Redis Enterprise Software.
Redis Enterprise architecture is built to provide a great deal of control with which to meet security regulations and standards.
One essential improvement that Redis Enterprise brings is the separation of paths for administrative access and data access. This separation equips Redis Enterprise with finer grain security controls, simplifying compliance and providing applications and developers with full access to one of the databases in the cluster to read and write data without requiring cluster administration privileges that may impact other databases/applications utilizing the same cluster (and vice versa).
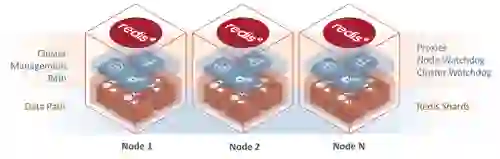
Figure: Redis Enterprise architecture showing the separate administration and data access paths.
With Redis Enterprise, security controls can be divided up into a few main areas to set up defenses: Authentication and Authorization; Encryption for “data in motion” and “data at rest”; Forensics and Logging. However, it should be said that despite all the security controls, if one does not secure the underlying infrastructure that Redis Enterprise utilizes then it will be hard to protect against any attack. It is important to follow security best practices to ensure a “defense in depth” strategy. Let’s explore how Redis Enterprise infrastructure can be secured first.
Defense in Depth
Even though Redis Enterprise provides a great deal of security controls, a fully secured deployment requires considering all attack vectors. To have a full defense against attacks, it is important to go beyond configuring Redis Enterprise security controls and secure the infrastructure itself.
Figure: Defensive firewalls at each border between public internet and the cluster internal network create the layers of defense.
In cyber security this is known as “defense in depth” and refers to placing layers of barriers between the attacker and the target. In this case, you are placing barriers at the edge of the data center, in the perimeter network and within the cluster internal network.
Authentication and Authorization with Redis Enterprise
In the Redis Enterprise security model, administrative access and data access paths are separated into two independent channels. This means that when it comes to authorization and authentication there are distinct paths.
Administrative Authentication and Authorization
Administrators authenticate to the UI, REST API or to the CLI using administrative accounts. Administrative identities can also be tied to central account management systems like LDAP stores. You can read more about how to configure LDAP-based accounts in Redis Enterprise here.
Redis Enterprise limits the administrative access to a set of ports that can be secured using additional OS-level mechanisms like IPTables, firewalls, etc.
Redis Enterprise provides role-based access control (RBAC). Each administrative identity in the system is also assigned to one of the built-in roles. You can find the list of available Redis Enterprise roles here.
Data Access Authentication and Authorization
Applications accessing data authenticate to the database endpoint using application passwords and certificates. When both certificate-based authentication and password is enabled, applications are required to present both factors of authentication to connect to the database.
For multi-tenant systems, each tenant can be isolated to access a subset of the databases in the system by assigning unique passwords and certificates to each database.
Source IP Filtering is another way data access can be controlled. With Redis Enterprise Cloud and Redis Enterprise VPC, administrators can limit the application server nodes that are allowed to connect to a database using IP filtering. This ensures that only application servers from a given source of IPs are eligible to authenticate to the database.
Encryption with Redis Enterprise
Redis Enterprise provides built-in encryption for data on the wire (data in motion) and data on disk (data at rest).
Encryption of Data in Motion
TLS/SSL-based encryption can be enabled for data in motion.
Encryption of Data at Rest
Encryption at rest is also available in Redis Enterprise VPC with a simple checkbox. In Redis Enterprise Software, admins can encrypt data at rest using transparent filesystem encryption capabilities available on linux OS.
Forensics and Event Logging with Redis Enterprise
Redis Enterprise provides a detailed set of logs, alerts and tracing facilities to help track administrative actions, from topology changes to modifications to cluster settings.
Redis Enterprise provides both alerts to track events in real time and stats to track real-time and historical trends, either rolled up to the cluster and database levels or at node and shard levels. Administrators in the system can view data up to a twelve-month window.
Security Compliance and Controls with Redis Enterprise DBaaS options
Redis provides the Redis Enterprise platform as a managed service on public cloud platforms. Redis Enterprise DBaaS provides topologies that can help simplify compliance with security standards in the public cloud. Customers get two types of deployment models:

Figure: Redis Cloud deployment model. Redis Enterprise is running under Redis’ cloud account.

Figure: Redis Enterprise VPC deployment model. Redis Enterprise is running under the customer’s cloud account.
We just scratched the surface of the many controls that Redis Enterprise provides for securing Redis. If you’d like to get a deeper dive into security best practices, you can join the webcast here.
Looking for details on Specter & Meltdown flaws? Visit our post on the topic here.